Imagine walking through a maze blindfolded—disorienting, inefficient, and time-consuming. This analogy can often describe the manufacturing process when companies lack a clear understanding of their workflow. Enter value stream mapping, a powerful tool that highlights each stage of the production process, revealing inefficiencies and opportunities for enhancement. In this blog post, we’ll get into the concept of Lean value stream mapping, exploring how it can revolutionize the manufacturing industry by streamlining operations, reducing waste, and ultimately, boosting productivity.
What is value stream mapping?
Value stream mapping (VSM), often referred to as information flow mapping, is a common Lean tool used to analyze and improve the flow of materials and information necessary to deliver a product or service to a customer.
By creating a visual representation of a process, known as a value stream map, value stream mapping helps you identify and eliminate waste. Thereby, improving efficiency and increasing customer satisfaction.
As a key component of the Lean methodology, value stream mapping provides a comprehensive overview of the entire production or service process. In essence, it enables you to identify areas for improvement and streamline operations for optimal performance.
History of value stream mapping
Value stream mapping has its origins rooted in the innovative practices of the Toyota Motor Corporation, a pioneer in manufacturing efficiency.
Early versions of diagrams that reveal the flow of materials and information in a production process can be traced back as early as 1918, highlighting the importance of material flow in the evolution of value stream mapping. These rudimentary diagrams laid the groundwork for what would become a highly sophisticated tool.
During the 1990s, value stream mapping became increasingly popular as businesses aimed to enhance efficiencies and streamline their operations. In fact, this period saw value stream mapping being widely adopted by high-efficiency business teams who recognized its potential to identify and eliminate waste. During this time, businesses constructed both current and future state value stream maps to identify areas of waste and design more efficient processes. Thus, optimizing production processes and enhancing overall performance.
Benefits of value stream mapping
Improved efficiency and productivity
One of the significant benefits of value stream mapping is its ability to improve efficiency and productivity by identifying and eliminating waste.
By creating your own value stream map, this visually represents the flow of your materials and information through a process, helping you to pinpoint non-value-adding activities and bottlenecks that slow down operations. In essence, this detailed insight enables you to streamline processes, reduce lead times, and increase throughput. This, in turn, ensures that resources are used more effectively.
Value stream mapping also fosters better communication and collaboration among team members as it provides a clear, shared understanding of the entire workflow. So, this collective insight enables teams to work together more effectively and aligns their efforts towards continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Cost reduction and increased revenue
Value stream mapping is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to reduce costs and increase revenue by eliminating waste and improving efficiency.
By visualizing the material and information flow, value stream mapping enables teams to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities. Thereby, focusing their time and resources on high-value tasks. This streamlined approach not only cuts down on unnecessary expenses, but also accelerates the production process. As a result, this allows for faster delivery of products and services.
Value stream mapping also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring consistent quality and timely fulfillment. As a result, this fosters customer loyalty and drives higher revenue.
Value stream mapping use cases
Manufacturing and production
Value stream mapping is a tool commonly employed in the manufacturing and production sectors to enhance efficiency and minimize waste. It involves creating a visual representation of the flow of materials and information through the production process, from raw materials to finished products.
By mapping out each step, teams can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and other inefficiencies that hinder productivity. This comprehensive overview enables teams to streamline processes, reduce lead times, and eliminate non-value-adding activities. Consequently, manufacturers can achieve a more efficient production system. Therefore, leading to significant cost savings and improved product quality.
Value stream mapping plays a crucial role not only on the production floor, but also in enhancing supply chain management and logistics. By applying value stream mapping principles to the entire supply chain, organizations can pinpoint and address inefficiencies in procurement, transportation, and inventory management. This holistic approach ensures that materials and products move smoothly and efficiently from suppliers to customers.
Software development and IT
Value stream mapping is a tool traditionally used in manufacturing, but has found significant applications in software development and IT.
By visualizing the flow of information and materials through the development process, value stream mapping helps teams identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and waste. In software development, this means mapping out every step from initial concept to deployment. For instance, this includes coding, testing, and review phases. By doing so, teams can pinpoint inefficiencies such as excessive wait times, overproduction of features, and underutilization of resources. Essentially, this detailed analysis allows for targeted improvements. Thus, leading to enhanced productivity and reduced development costs.
In addition to streamlining the development process, value stream mapping plays a huge role in optimizing the deployment pipeline. By mapping the entire deployment process, from code commits to live release, teams can identify and eliminate delays. Therefore, ensuring a smoother and faster transition from development to production. This reduction in time-to-market is crucial in today’s fast-paced tech environment, where being first can offer a significant competitive advantage. Moreover, improving the deployment process reduces downtime and enhances the reliability of software releases. Consequently, leading to higher customer satisfaction and better overall performance of IT systems.
The 8 types of waste value stream mapping helps you to identify
Value stream mapping is a common tool used in Lean methodology to identify and eliminate various types of waste within a process The 8 wastes of Lean manufacturing, which can be identified through value stream maps, include:
- Defects: Errors that result in rework or scrap, leading to wasted materials and time.
- Overproduction: Producing more than is needed or before it is needed, which ties up resources and leads to excess inventory.
- Waiting: Idle time when resources such as people, machines, or materials are not in use, causing delays and inefficiencies.
- Non-utilized talent: Underutilizing employees’ skills and knowledge, which can hinder innovation and problem-solving.
- Transport: Unnecessary movement of materials or products between processes, which does not add value and consumes time and resources.
- Inventory: Excess products or raw materials that are not being processed, which can lead to increased storage costs and potential obsolescence.
- Motion: Unnecessary movements by people, such as reaching or walking, which do not add value and can cause fatigue and injury.
- Excess processing: Performing more work or using more resources than necessary to meet customer requirements, which leads to inefficiency and waste.
Standard value stream mapping symbols
Value stream mapping utilizes a set of standardized symbols to represent different elements of the process, such as the flow of materials and information. These symbols, including icons for processes, inventory, and information flows, help ensure consistency and clarity in communicating the steps and interactions within a value stream.

How to create a value stream map: A step-by-step guide
Creating a value stream map is an essential technique used in Lean process management to visualize and analyze the flow of materials and information currently necessary to bring a product or service to a consumer. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a value stream map in nine steps:
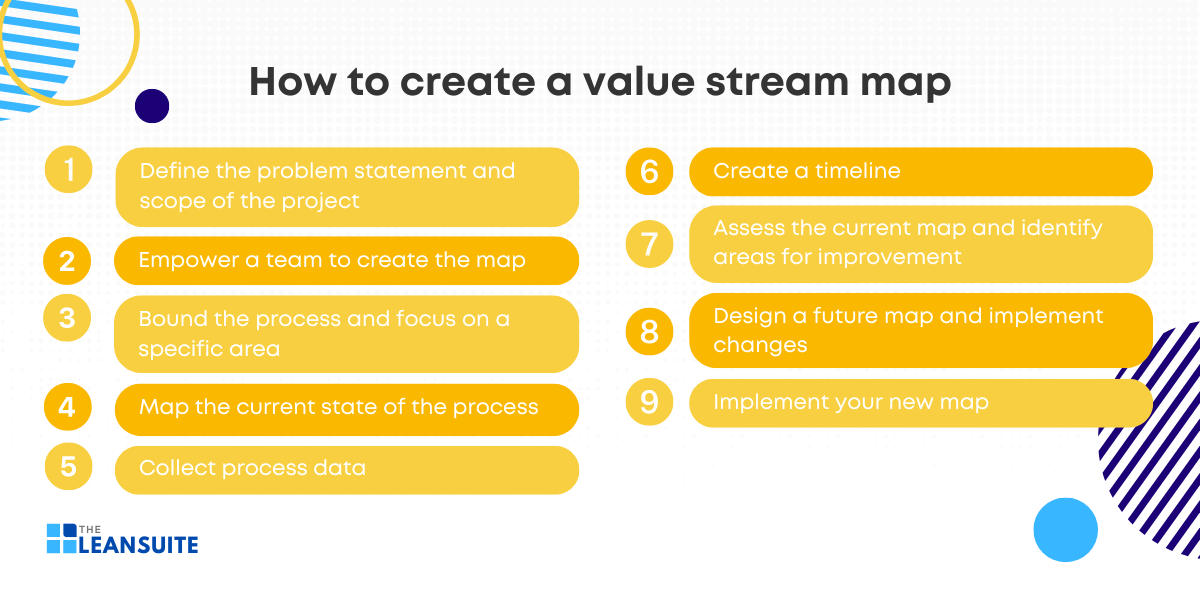
1. Define the problem statement and scope of the project
Begin by clearly identifying the problem that needs to be addressed. Essentially, this involves understanding the issue at hand and determining how it affects the overall process. The problem statement should be concise and focused, outlining the specific goals you aim to achieve.
Additionally, defining the scope of the project is crucial; it sets the boundaries of what will be included in the value stream map and ensures that the team remains focused on relevant areas.
2. Empower a team to create the map
Assemble a cross-functional team that includes individuals from various departments and levels within your organization. This team should have a deep understanding of the process being analyzed and possess the authority to make decisions and implement changes.
Empowering the team involves providing them with the necessary tools, training, and support to effectively create the value stream map. In short, a diverse and knowledgeable team can offer different perspectives and insights. Thus, leading to a more comprehensive and accurate map.
3. Bound the process and focus on a specific area
Clearly define the start and end points of the process you are mapping. This step involves selecting a specific area of the process to focus on, ensuring that the scope is manageable and the analysis is thorough.
By setting boundaries, you prevent the project from becoming too broad or unwieldy, allowing the team to concentrate on a well-defined segment of the process. This focused approach enables a more detailed examination of the current state and facilitates the identification of key areas for improvement.
4. Map the current state of the process
Create a visual representation of the existing process, capturing all the steps, activities, and flow of materials and information. This current state map should include details such as cycle times, inventory levels, and handoffs between departments.
Gathering input from the team and directly observing the process are essential for ensuring the accuracy of the map. The goal is to gain a clear understanding of how the entire process currently operates, highlighting any inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or delays. Moreover, make sure to use standard value stream mapping symbols to ensure clarity and consistency.
5. Collect process data
Gather quantitative and qualitative data related to the process. This includes metrics such as lead times, cycle times, defect rates, and work-in-progress levels. Collecting data may involve conducting time studies, reviewing historical records, and interviewing employees.
Accurate data collection is critical for identifying areas of waste and variability within the process. Essentially, the data serves as a baseline for assessing the current state and measuring the impact of future improvements.
6. Create a timeline
Develop a timeline at the bottom of your value stream map that aligns with the current state map, illustrating the sequence and duration of each process step. This timeline should highlight the total lead time, including both value-added and non-value-added activities.
By visualizing the flow of time, the team can identify periods of waiting, delays, and other inefficiencies. Basically, the timeline provides a clear picture of the process’s overall performance and helps prioritize areas for improvement.
7. Assess the current map and identify areas for improvement
Analyze the current state map and timeline to pinpoint sources of waste, inefficiencies, and areas that do not add value to the customer.
Engage the team in a collaborative discussion to identify root causes and brainstorm potential solutions. Look for opportunities to streamline the process, reduce the cycle time, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency.
This assessment phase is critical for developing a clear understanding of the process’ weaknesses and potential areas for enhancement. continuous improvement.
8. Design a future map and implement changes
Create a new map that represents the ideal state of the process after improvements have been made. This future state map should incorporate the identified solutions and outline a more efficient, streamlined process flow.
Involve the team in designing this map. This, in turn, ensures that proposed changes are realistic and achievable. Once the future state map is finalized, develop an action plan for implementing the changes. For instance, this may include assigning responsibilities, setting timelines, and establishing metrics for success.
9. Implement your new map
Put the action plan into practice. In other words, make the necessary changes to the process as outlined in the future state map. This may involve process re-engineering, adopting new technologies, retraining employees, or reorganizing workflows.
Monitor the implementation closely, tracking progress and measuring the impact of the changes. Continuous improvement is key. So, always look for further opportunities to enhance the process. In addition, continuously engage the team and stakeholders, addressing any challenges that arise and making adjustments as needed.
In sum, successful implementation of the new map leads to a more efficient, effective process that delivers greater value to the customer.
Value stream mapping best practices
Empower teams and stakeholders
Empowering teams and stakeholders is essential for successful value stream mapping. This is because it fosters a sense of ownership and accountability throughout the process. When teams are given the autonomy to make decisions and implement changes, they become more invested in the outcomes and are likely to contribute innovative solutions. This empowerment leads to a more dynamic and responsive improvement process, as teams can act swiftly on insights gained from the value stream mapping.
Furthermore, involving stakeholders ensures that their needs and expectations are integrated into the process. Therefore, creating a more holistic and effective approach to the value stream analysis. By actively engaging both teams and stakeholders, you can harness a wealth of knowledge and experience, resulting in a more accurate and actionable value stream map.
Focus on customer value
Value stream mapping should primarily focus on delivering customer value, as this is the ultimate measure of an organization’s success. To achieve this, teams must identify and eliminate waste that does not contribute to customer satisfaction. In other words, this means examining every step in the process to ensure it adds value from the customer’s perspective.
The goal of value stream mapping is to streamline the flow of materials and information. Thereby, reducing delays and inefficiencies that hinder meeting customer demand. By concentrating on customer value, you can enhance your competitiveness and build stronger relationships with your customers.
Ultimately, a value stream map that prioritizes customer value will lead to more efficient processes, higher quality products, and increased customer satisfaction.