Agile project management has revolutionized the way teams approach the complexities of modern projects. By emphasizing collaboration, flexibility, and customer-centric development, Agile methodologies have become the foundation for successful project delivery. In this blog post, we will explore the 12 key principles of Agile project management, uncovering how these foundational guidelines empower teams to adapt swiftly to changing requirements, foster innovation, and enhance productivity.
What is Agile project management?
Agile project management is a flexible and iterative method for managing projects. It focuses on adaptability, teamwork, and ensures customer satisfaction.
Unlike traditional project management methods that often rely on rigid planning and sequential workflows, the Agile process focuses on delivering small, incremental updates and improvements. This method fosters continuous feedback and allows teams to respond quickly to changing requirements or unforeseen challenges.
By breaking projects into manageable units called “sprints,” Agile teams can enhance flexibility, ensure timely delivery, and maintain a strong focus on delivering high-quality outcomes that align closely with customer needs and expectations.
The four core values of Agile project management
Agile project management is built upon a set of core values that guide teams in delivering high-quality results while fostering a collaborative and adaptable work environment. These values, as articulated in the Agile Manifesto, emphasize the importance of people, communication, and flexibility over traditional, rigid processes. Let’s explore the four core values of Agile project management:

1. Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
This value highlights the significance of people and their collaboration in the success of a project. While processes and tools are important, Agile places greater emphasis on empowering individuals and fostering effective communication within the team.
- Focus on team dynamics: Building strong relationships and trust among team members is crucial. In other words, by encouraging open communication and collaboration, this allows team members to share ideas and address challenges more effectively.
- Adaptability: Since individuals are more adaptable than rigid processes, Agile teams are better equipped to respond to changes and unexpected issues.
- Empowerment: By valuing individuals and their interactions, Agile promotes a culture where team members feel empowered to take initiative and make decisions.
2. Working software over comprehensive documentation
Agile prioritizes delivering functional software that meets customer needs, emphasizing the principle to deliver working software frequently over spending excessive time on documentation. So, while documentation has its place, the primary focus is on creating a product that works and delivers value.
- Efficiency: Agile teams aim to produce working software quickly and iteratively. Therefore, allowing for continuous feedback and improvement.
- Customer satisfaction: By focusing on delivering working software, Agile teams ensure that customers receive tangible results that meet their expectations.
- Iterative development: Instead of relying solely on detailed upfront documentation, this approach allows for ongoing improvements and refinements based on real-world use and feedback.
3. Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Agile values ongoing collaboration with customers throughout the project lifecycle rather than adhering to strict contract terms. As a result, this ensures that the final product aligns with customer needs and expectations.
- Continuous engagement: Regular interactions with customers help maintain alignment with their evolving requirements and priorities.
- Flexibility: Agile teams can make adjustments based on customer feedback. Thereby, leading to a more satisfactory outcome.
- Building relationships: By prioritizing collaboration, Agile fosters strong partnerships with customers. This, in turn, leads to mutual trust and better understanding of project goals.
4. Responding to change over following a plan
Agile processes harness change as a natural part of development, recognizing that customer needs and market conditions often evolve. Consequently, Agile teams are prepared to adapt their plans to accommodate these changes.
- Adaptability: Agile methodologies provide the flexibility to adjust strategies and priorities as needed. Thus, ensuring that the project remains relevant and valuable.
- Iterative planning: Agile teams frequently reassess and adjust their plans based on new insights and feedback. In doing so, this allows them to stay aligned with project goals.
- Innovation: By welcoming change, Agile encourages innovation and creative problem-solving, leading to more effective solutions.
The 12 key principles of Agile project management
By adhering to the 12 key principles of Agile project management, teams can navigate the complexities of modern project environments and adapt to changing requirements effectively.
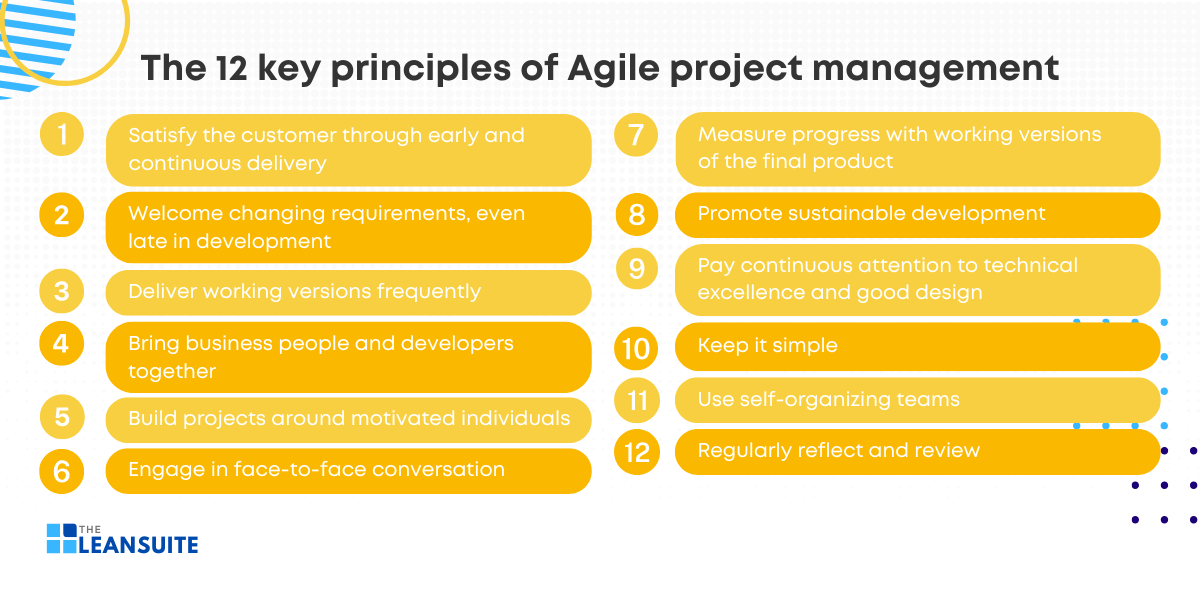
1. Satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery
One of the fundamental principles of Agile project management is to prioritize customer satisfaction by delivering valuable software early and consistently. By prioritizing customer needs over a “we know best” mindset, Agile teams can adapt quickly and ensure their work aligns with customer expectations. This approach leads to more frequent delivery of value, increased customer satisfaction, and a feedback loop that minimizes later changes, enhancing project success.
2. Welcome changing requirements, even late in development
Agile project management encourages flexibility by welcoming changes in requirements. In fact, it even encourages this during the later stages of development. This principle recognizes that customer requirements can shift throughout the project lifecycle, and it’s crucial for development teams to adapt their plans accordingly. By embracing change, teams can ensure that the final product remains relevant and effective. Ultimately, leading to higher customer satisfaction and a more successful outcome.
3. Deliver working versions frequently
The third principle of Agile project management emphasizes the importance of delivering working versions of a product frequently, a key aspect of Agile projects. This approach, central to the Agile mindset, involves breaking projects into smaller, manageable portions known as “sprints.” Each sprint concludes with the delivery of a working version of the product. Thereby, enabling teams to continuously deliver value and gather feedback.
By breaking down large projects into these iterative cycles, Agile teams can adapt more readily to changes and ensure that the final product closely aligns with customer needs and expectations. This principle enhances flexibility and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration within teams. Thus, making it a fundamental aspect of the principles of Agile project management and effective Agile practices.
4. Bring business people and developers together
Collaboration between business stakeholders and developers is essential in Agile project management. By fostering open communication, these two groups can work together to remove uncertainties and align their efforts with the project’s goals and objectives. What’s more, this collaboration ensures that both the technical and business perspectives are considered. As a result, this allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the project’s requirements.
5. Build projects around motivated individuals
Agile project management emphasizes the importance of motivated and empowered team members. By creating a supportive environment that values individual contributions, teams can harness the creativity and expertise of their members. Consequently, this principle leads to innovative solutions and high-quality results, as motivated individuals are more likely to take initiative and produce exceptional work.
6. Engage in face-to-face conversation
Face-to-face communication is highly valued in Agile project management. This is because it facilitates clear and efficient information exchange. In-person interactions help build trust and understanding among team members. Thus, enabling them to address challenges collaboratively and effectively. In short, this principle ensures that communication remains a priority, reducing the chances of misunderstandings and enhancing overall team dynamics.
7. Measure progress with working versions of the final product
In Agile project management, progress is measured by the delivery of working software rather than extensive documentation. In short, this principle keeps the focus on delivering tangible value and allows teams to make adjustments based on real-world use and feedback. By prioritizing working software, teams can maintain a clear understanding of their progress and ensure that the project remains on track.
8. Promote sustainable development
Agile methodologies advocate for sustainable development practices that maintain a consistent pace throughout the project. By avoiding burnout and maintaining a steady workflow, teams can deliver high-quality results without sacrificing the well-being of their members. This approach ensures long-term productivity and helps prevent the negative impacts of overworking.
9. Pay continuous attention to technical excellence and good design
The principles of Agile project management highlights the importance of technical excellence and thoughtful design in delivering high-quality results. In essence, it advocates for a relentless focus on refining technical skills and ensuring that design processes are robust and well-considered. By continuously testing and monitoring, teams can identify and resolve issues early in the development cycle. Thereby, minimizing the risk of defects and enhancing overall product quality.
10. Keep it simple
Simplicity is a key principle of Agile project management, as it helps teams focus on what truly matters. By eliminating unnecessary complexity, Agile teams can streamline their processes and deliver more efficient, effective solutions. Basically, this principle encourages teams to prioritize essential features and functionality. This, in turn, results in a product that meets customer needs without unnecessary tasks that don’t add value.
11. Use self-organizing teams
Agile methodologies empower teams to organize themselves, leveraging their collective expertise to make decisions and solve problems. This principle fosters creativity, accountability, and a sense of ownership. As a result, this leads to better project outcomes. By encouraging self-organization, Agile project management creates an environment where teams can thrive and produce their best work.
Additionally, Agile managers shouldn’t need to micromanage a project team. Instead, they should provide guidance and support while trusting the team to manage their tasks and responsibilities effectively. This trust in self-organizing teams enhances productivity and motivates team members to take initiative and innovate.
12. Regularly reflect and review
The twelfth and final principle of Agile project management emphasizes the importance of regularly reflecting and reviewing, a practice that is integral to the principles of Agile project management.
Most Agile frameworks incorporate a retrospective at the end of each phase or sprint, providing a structured opportunity for teams to assess their performance. During these retrospectives, teams review what went well and what didn’t. Consequently, this fosters open discussions about areas for improvement.
This principle’s focus on continuous improvement ensures that teams remain adaptable, consistently seeking ways to enhance their processes and work. By encouraging a culture of reflection and learning, this principle empowers teams to evolve and refine their practices. Ultimately, driving greater project success.
Types of Agile methodologies
Agile methodologies provide diverse frameworks suited to different project environments. Each have unique principles and practices to enhance productivity and adaptability. Below are five distinct types of Agile methodologies:
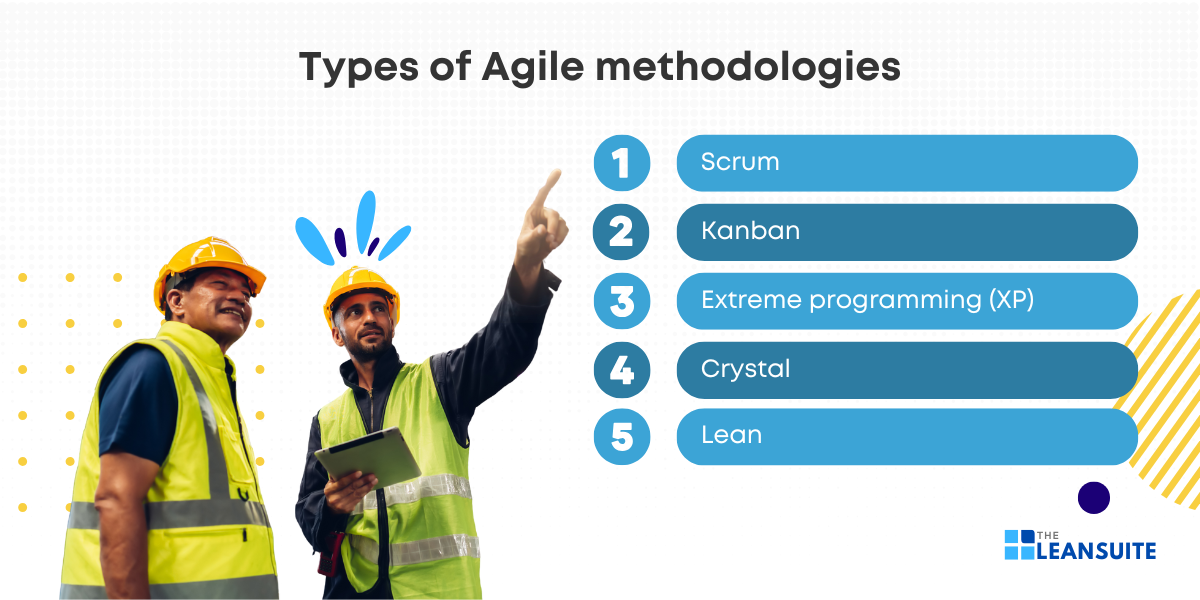
1. Scrum
- Overview: Scrum is one of the most popular Agile methodologies and is primarily used in software development. It focuses on iterative progress through sprints, which are fixed-length iterations, typically lasting 2-4 weeks.
- Key features: Scrum emphasizes roles such as the Scrum Master and Product Owner to facilitate team collaboration and prioritize work. Essentially, it involves regular ceremonies, including daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, and retrospectives, to ensure continuous improvement and alignment.
2. Kanban
- Overview: Kanban is a visual process management methodology that aims to optimize the flow of work and improve efficiency without overhauling existing processes.
- Key features: It employs a Kanban board to visualize work, limit work in progress (WIP), and manage flow. Kanban encourages incremental changes and continuous delivery without set iterations. Therefore, making it highly adaptable to changing requirements.
3. Extreme programming (XP)
- Overview: Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology that prioritizes technical excellence and customer satisfaction through frequent releases and close collaboration.
- Key features: XP emphasizes practices such as pair programming, test-driven development, continuous integration, and frequent communication with customers. It aims to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer needs.
4. Crystal
- Overview: Crystal is a family of Agile software development methodologies that focus on the importance of people and their interactions over processes and tools. It adapts to team size, project priorities, and criticality.
- Key features: Crystal emphasizes frequent delivery, reflective improvement, and osmotic communication. It is flexible, with variations like Crystal Clear, Crystal Yellow, and Crystal Orange, each tailored to different project contexts and team sizes.
5. Lean
- Overview: Lean, also known as Lean process management, is an Agile methodology derived from Lean manufacturing principles. Basically, it focuses on delivering maximum value to the customer with minimal waste.
- Key features: Lean emphasizes value stream mapping, eliminating waste, and optimizing processes. It promotes continuous improvement and respect for people, encouraging teams to focus on efficiency and value delivery.
Benefits and best practices of Agile project management
Agile project management offers numerous benefits, making it an ideal approach for teams that thrive on rapid progress and require less rigid structures and deadlines.
By fostering an environment of flexibility and adaptability, Agile methodologies are particularly suitable for projects that demand consistent communication and a more responsive approach to change. Ultimately, enhancing the customer’s competitive advantage.
One of the key advantages of Agile is its emphasis on self-organizing teams that focus on delivering working software frequently. This ensures that value is consistently provided to customers. Furthermore, Agile project management focuses on maximizing value by eliminating waste and improving efficiency, aligning closely with the principles of Lean thinking.
By embracing these best practices, Agile teams can enhance their productivity, foster innovation, and deliver high-quality outcomes that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations.