Lean organizations are masters of efficiency. That is to say, they embody a philosophy that transforms the way businesses operate in a constantly changing marketplace. By focusing on continuous improvement and waste reduction, these organizations harness key attributes that enable them to thrive amidst challenges. In this blog post, we will explore the top five characteristics of a lean organization.
Defining lean organizations
A lean organization uses a business process methodology centred around maximizing efficiency while minimizing waste. This business process methodology is known as lean process management or lean manufacturing. It emphasizes the importance of streamlining operations by eliminating processes that do not add value. Thereby, optimizing the use of resources.
By focusing on continuous improvement and adaptability, lean organizations are well-equipped to respond effectively to changing market demands. What’s more, the lean philosophy encourages businesses to foster a culture of innovation and flexibility. Therefore, enabling them to remain competitive and resilient in a dynamic marketplace.
Through the implementation of lean principles, these organizations are able to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. Ultimately, leading to greater customer satisfaction and business success.
Key principles of lean organizations
Lean organizations are guided by a set of key principles that emphasize creating value through a meticulous focus on what truly matters.
At the heart of lean thinking is the commitment to continuously make small, incremental improvements to enhance processes and interactions (also known as continuous improvement). This ongoing refinement ensures that operations remain efficient and responsive to change.
By prioritizing the customer’s needs, lean organizations aim to maximize value creation while minimizing waste. This involves eliminating unnecessary steps and optimizing resources to deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
In short, the lean philosophy fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering organizations to remain agile and competitive in a dynamic marketplace.
Embracing lean principles
Lean organizations recognize the importance of embracing lean principles to drive growth and efficiency. These principles serve as the foundation of a lean organization’s decision-making process. In other words, it guides efforts to eliminate waste, improve production processes, and increase customer satisfaction.
Originally rooted in manufacturing, particularly through the Toyota Production System (TPS), lean principles and process management systems have been widely adopted across various industries and sectors. The widespread acceptance of these practices highlights their success in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
The five principles of lean
Lean principles serve as a guiding framework for organizations striving to enhance efficiency and value creation. These principles are rooted in the philosophy of continuous improvement and waste elimination. Below, we outline the five key principles of Lean:
1. Define value
The first principle of lean involves identifying what truly matters to the customer. By understanding the customer’s needs and preferences, organizations can define what represents value from the customer’s perspective. In doing so, this ensures that all efforts are aligned with delivering products or services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
2. Map the value stream
Mapping the value stream involves analyzing the entire production process to identify all steps involved in delivering the final product or service. In other words, this process helps in pinpointing areas of waste, inefficiency, or redundancy that do not add value. As a result, organizations can focus on optimizing processes to enhance overall efficiency.
3. Create flow
After mapping the value stream, the next step is to ensure that the production process operates seamlessly and is free from interruptions or delays. By creating a seamless flow, this eliminates bottlenecks and ensures that each step efficiently transitions into the next. This results in faster production times and improved resource utilization.
4. Establish pull
Establishing pull means producing based on actual customer demand rather than forecasts. Basically, this approach minimizes excess inventory and reduces the risk of overproduction, which can lead to waste. By responding directly to customer needs, organizations can ensure that they deliver products that are both timely and relevant.
5. Seek perfection
The final principle of lean is about striving for continuous improvement. Lean organizations are committed to seeking perfection by regularly assessing performance and making incremental improvements. This ongoing pursuit of excellence ensures that organizations remain competitive, adaptable, and capable of providing high-quality products and services to their customers.
What are the characteristics of a lean organization?

1. Focused on customer value
Lean organizations prioritize customer value above all else. They understand that it is the key driver for other business metrics and indicators. In essence, every decision made within a lean organization involves a thorough assessment of how it will impact the customer.
This customer-centric approach ensures that products and services meet or exceed expectations. Thereby, fostering customer loyalty and satisfaction. By making customer value the foundation of their decision-making process, lean organizations can continuously align their goals and strategies with the needs and desires of their customer base.
2. Collaborative and engaged
One of the fundamental characteristics of a lean organization is their commitment to breaking down silos and fostering a culture of cross-functional collaboration and communication.
By creating this type of work environment, this makes employees feel empowered to share their knowledge and experiences across the entire organization. Thus, leading to a more informed and cohesive workforce. This collaborative spirit is essential for tackling the biggest challenges and driving innovation.
By encouraging teamwork and open dialogue, lean organizations can harness the collective expertise of their frontline employees to improve processes and achieve organizational goals.
3. Data-driven decision making
Lean organizations rely heavily on data-driven decision-making processes to move the continuous improvement process forward. In fact, they leverage various lean management tools such as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), A3 problem-solving, Catchball, and Hoshin Kanri to ensure that improvement work is both effective and consistent across the organization.
By embedding a methodology for improvement work, lean organizations can systematically analyze data, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes that lead to better outcomes. This systematic method ensures that improvement initiatives are consistent and in line with the strategic goals of the organization.
4. Proactive and adaptable
One of the defining characteristics of a lean organization is the emphasis on inspecting processes rather than products. As a result, this prevents problems and eliminates waste. This approach empowers employees to identify and act on opportunities for process improvements. Therefore, creating proactive lean organizations that are agile and adaptable.
What’s more, employees are encouraged to speak up and take the time to make improvements. In doing so, this fosters an environment of safety and innovation. By embracing adaptability, lean organizations can quickly respond to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive edge.
5. Continuous improvement mindset
A continuous improvement mindset is deeply ingrained in lean organizations. That is to say, a lean organization recognizes that there is always room for improvement, even when performance is strong.
Leaders play a key role in encouraging employees to seek out opportunities for further success through continuous improvement. The Kaizen philosophy, which emphasizes ongoing, incremental improvements, is central to this mindset.
By fostering a lean culture that values continuous improvement, lean organizations can enhance their processes, products, and services.
Implementing lean successfully
Successfully implementing lean principles requires a strategic approach that emphasizes planning, commitment, and continuous improvement. To truly embody the characteristics of a lean organization, you must adopt a holistic mindset that facilitates change at every level. This includes everyone from leadership to frontline employees. The following steps outline a comprehensive pathway to successful lean implementation:
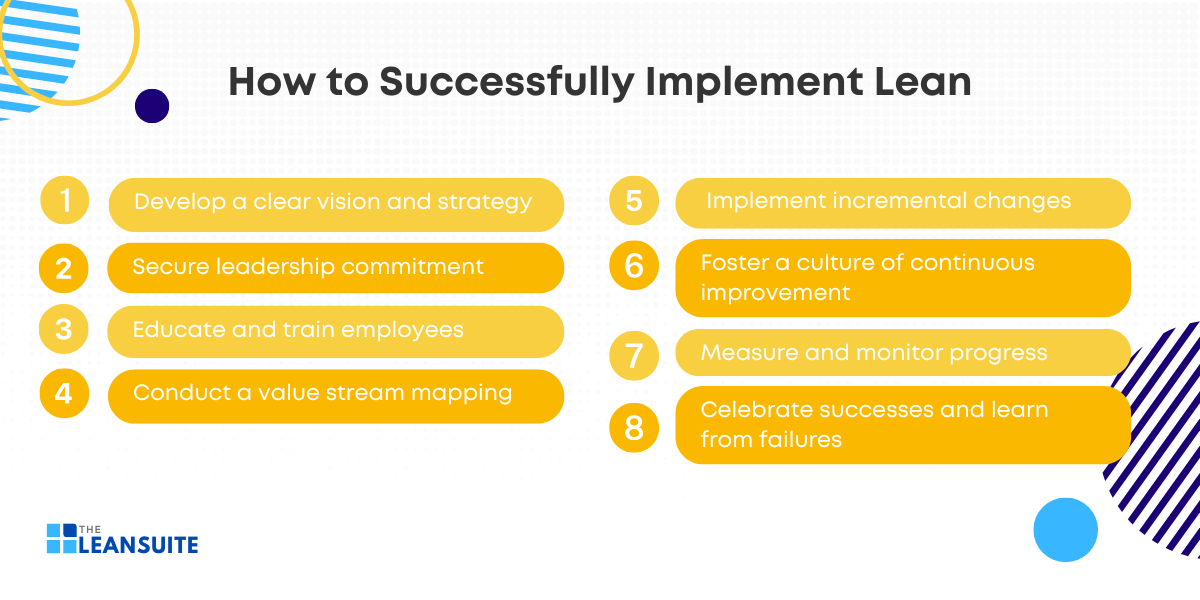
1. Develop a clear vision and strategy
Before initiating lean practices, it is important to define a clear vision and strategy that aligns with your organization’s goals. This involves understanding the core purpose of adopting lean—whether it’s to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, or all of these.
Establishing a strategic roadmap ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page and committed to the lean transformation process.
2. Secure leadership commitment
Strong leadership is integral to the success of lean implementation. Your leaders must champion the lean philosophy and set an example for the rest of your organization. For instance, this involves providing resources, support, and encouragement for lean initiatives.
Leadership commitment also includes fostering a culture that embraces change and innovation. As a result, this empowers employees to contribute to continuous improvement.
3. Educate and train employees
Lean implementation is a collective effort that requires involvement from all levels of your organization. That’s why providing comprehensive training and education on lean principles and tools is essential.
Employees should understand concepts of lean systems such as value stream mapping, 5S, Kanban, and Kaizen. This is because training empowers employees to identify waste, suggest improvements, and participate actively in lean processes.
4. Conduct a value stream mapping
Value stream mapping is a critical step in identifying areas of waste and inefficiency. By analyzing the entire production process, you can pinpoint steps that do not add value and need optimization. Moreover, this mapping exercise provides a visual representation of the current state and helps in designing a future state that enhances flow and efficiency.
5. Implement incremental changes
Lean is not about drastic changes but rather incremental improvements. So, start by implementing small, incremental changes that can generate quick wins and build momentum.
This approach helps in gaining employee buy-in and demonstrates the tangible benefits of lean initiatives. Continuous assessment and refinement helps to ensure that these changes become part of the organization’s everyday practices.
6. Foster a culture of continuous improvement
A successful lean organization thrives on a culture of continuous improvement. This improvement process is also often referred to as Kaizen.
Encourage employees to regularly assess processes and seek opportunities for improvement. This mindset leads to sustained growth and allows you to remain agile and responsive to market changes.
7. Measure and monitor progress
To ensure the success of lean implementation, it is important to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly monitor progress. These metrics help in assessing the effectiveness of your lean initiatives and identifying areas that require further improvement.
Regular reporting and feedback loops keep everyone informed and aligned with your organization’s lean goals.
8. Celebrate successes and learn from failures
Recognizing and celebrating successes is key to maintaining morale and encouraging ongoing participation in lean initiatives. Similarly, it’s essential to view failures as learning opportunities and address them constructively.
By fostering an environment where experimentation is encouraged, you can continually refine your own lean manufacturing practices and drive innovation.