Enhancing efficiency and profitability is crucial for manufacturing companies to maintain their growth and sustainability. As companies aim to streamline their operations and maximize output, emphasizing key production metrics becomes crucial. One such vital metric is throughput time, which measures the time taken to complete a production process from start to finish. In this blog post, we will explore effective strategies to improve throughput time, enabling you to identify and eliminate bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enhance productivity, and ultimately increase output without compromising on quality.
What is throughput time?
Throughput time is the total amount of time it takes for a product to move through the entire production process from start to finish. It encompasses all the various steps and stages involved in production, making it a comprehensive measure of manufacturing efficiency.
For instance, in a manufacturing setting, if a company produces custom furniture, the throughput time would encompass the period from the moment you start making it, to the moment the finished piece is ready to get shipped out to the client.
Essentially, throughput time is used to identify a company’s rate of production or the speed at which something is processed. Also, it’s important to note that it only looks at completed items, not work in progress.
This metric can be broken down into four key components:
- Processing time: The actual time spent working on the product
- Move time: The duration taken to transport the product between different stages, as well as the time workers spend moving to and from their posts
- Inspection time: The period used for quality inspections, examining the products for any damage and inconsistencies
- Wait time: The idle time the product spends waiting for the next process to begin
How to calculate throughput time
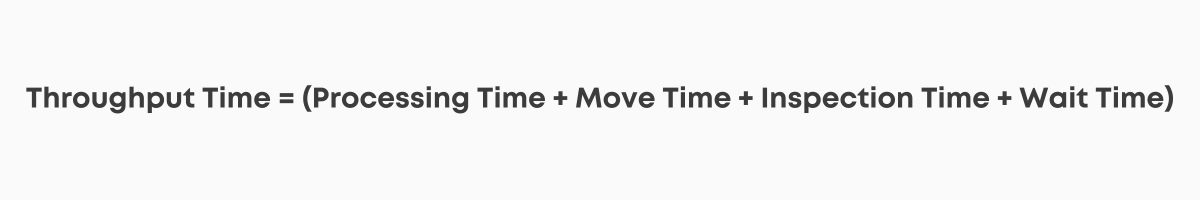
For example, in a car manufacturing plant, if it takes:
- 10 hours to assemble a car
- 2 hours to move it between different workstations
- 1 hour for quality inspections, and
- 5 hours waiting for various processes to start
The total throughput time would be (10hrs + 2hrs + 1hr + 5hrs) or 18 hours.
Throughput time vs cycle time
Throughput time and cycle time are often used interchangeably because they both measure the duration needed to complete a process from start to finish. However, there is a subtle difference between the two.
Throughput time refers to the overall time a product or service takes to pass through an entire system, including all waiting and processing times. Cycle time, on the other hand, zeroes in on the time required to complete a specific part of that process.
While it’s largely a matter of preference which term to use, the context can dictate the more appropriate choice. For instance, in manufacturing, cycle time might be used to focus on improving the efficiency of a particular workstation, whereas throughput time could be more relevant when assessing the performance of the entire production line.
Throughput time vs lead time
Lead time is another important metric often used in project management and manufacturing to measure efficiency and performance.
Lead time begins when customer orders are received and ends when the product is delivered to their doorstep. However, throughput time solely focuses on the manufacturing process itself. That is to say, lead time takes into account any waiting periods before manufacturing and after it too.
In essence, while throughput time focuses on the efficiency of the process itself, lead time takes a broader view, considering external factors that might affect the overall timeline.
The importance of improving manufacturing throughput
Production throughput is key metric for measuring operational excellence in manufacturing operations. Here are several key reasons why you should improve manufacturing throughput:
Increased efficiency and productivity
Enhancing manufacturing throughput means that you can produce more products in less time. So, this increase in efficiency allows you to meet higher customer demand levels without the need for additional resources or excessive overtime. What’s more, streamlined processes and reduced bottlenecks lead to a smoother production flow. As a result, this enables your workers and machinery to operate at optimal capacity.
Cost reduction
Improved manufacturing throughput often results in significant cost savings. By minimizing downtime and reducing waste, you can lower your production costs. For example, this includes savings on labor, energy, and materials. Additionally, higher manufacturing throughput can lead to better utilization of existing equipment. Therefore, delaying the need for expensive capital investments in new machinery.
Enhanced customer satisfaction
Faster production times mean quicker delivery of products to your customers. This, in turn, can lead to higher customer satisfaction as orders are fulfilled more promptly and reliably. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations can foster loyalty and repeat business, which is crucial for sustaining long-term growth and competitiveness in the market.
Quality improvement
When you focus on improving manufacturing throughput, it often involves refining and standardizing processes, which can lead to higher product quality. In other words, consistent and efficient processes reduce the likelihood of errors and defects. This ensures that the final products meet quality standards. High-quality products enhance your company’s reputation and reduce costs associated with returns and rework.
5 ways to improve your throughput time
If you’re a manufacturing manager, it’s likely that your goals are to increase throughput and decrease throughput time. As such, there are various strategies to help you achieve these goals. Here are some of the best ways you can go about improving this metric:

1. Optimize the production process
Optimizing the production process to improve throughput time involves a strategic approach centred on efficiency and waste reduction.
One effective method is implementing Lean manufacturing principles, which focus on eliminating non-value-added activities and streamlining workflows. This can be achieved by mapping out the entire production process, identifying bottlenecks, and reconfiguring the shop floor layout to minimize movement and wait times.
Process improvement tools and methods like Lean Six Sigma can also play a vital role in this strategy. Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of Lean manufacturing with Six Sigma’s data-driven approach to quality control. By systematically applying these methodologies, you can identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and enhance overall efficiency.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous improvement among employees ensures that the workforce is always looking for ways to refine processes. Ultimately, leading to more efficient and faster production cycles.
2. Improve employee training and development
To improve throughput time, it is important to improve employee training and development.
Proper training for frontline workers on production lines is essential as it equips them with the skills and knowledge required to perform their tasks efficiently and accurately. By educating these workers, companies can significantly reduce errors, minimize downtime, and streamline production processes.
Well-trained employees are better prepared to handle complex machinery, troubleshoot issues swiftly, and maintain quality standards, all of which contribute to faster and more reliable production cycles. This not only boosts overall throughput, but also empowers the workforce to make informed decisions that can drive critical business strategies. For instance, expanding work capacity or accelerating production schedules.
3. Leverage technology
Implementing automated production systems is a strategic approach to improve production throughput and minimize equipment downtime.
By using factory automation and integrating advanced robotics, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance technologies, factories can achieve higher efficiency and reliability. What’s more, automation enables continuous operation with minimal human intervention. Therefore, leading to consistent production rates and faster turnaround times.
Additionally, leveraging a Lean enablement software can further optimize these processes by embedding Lean principles into daily operations. This software helps identify and eliminate waste, streamline workflows, and promote continuous improvement.
In short, automation supported by a Lean enablement software can dramatically increase manufacturing throughput, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity and operational efficiency. Thus, fostering a more agile and responsive production environment.
4. Reduce equipment downtime
Reducing equipment downtime is crucial for improving throughput time in any production environment.
Machines and equipment can deteriorate and break down over time due to frequent and prolonged use, leading to significant disruptions in the production process. So, by ensuring that machines and equipment are well-maintained, businesses can substantially minimize these downtimes. Therefore, maintaining a more consistent and efficient production flow.
Leveraging predictive maintenance, a proactive approach that utilizes data and analytics to forecast equipment failures, can further enhance this process. By predicting when equipment is likely to fail, businesses can schedule routine maintenance activities in advance, mitigating unplanned breakdowns and ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently.
5. Reduce rejected parts
A high parts rejection rate can significantly slow down the entire production process and reduce manufacturing throughput.
When a large number of parts are deemed unusable, it disrupts the workflow, causing delays as defective parts are identified, separated, and replaced. This not only hampers the efficiency of the assembly line, but also increases operational costs and wastes valuable resources. Thus, reducing the parts rejection rate is critical to improving the overall production process, maximizing throughput, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Implementing stringent quality control measures and utilizing data and analytics to pinpoint areas for improvement can help identify the root causes of defects. By addressing these issues and making necessary changes, you can enhance product quality, improve throughput time, streamline production, and meet customer expectations more consistently.