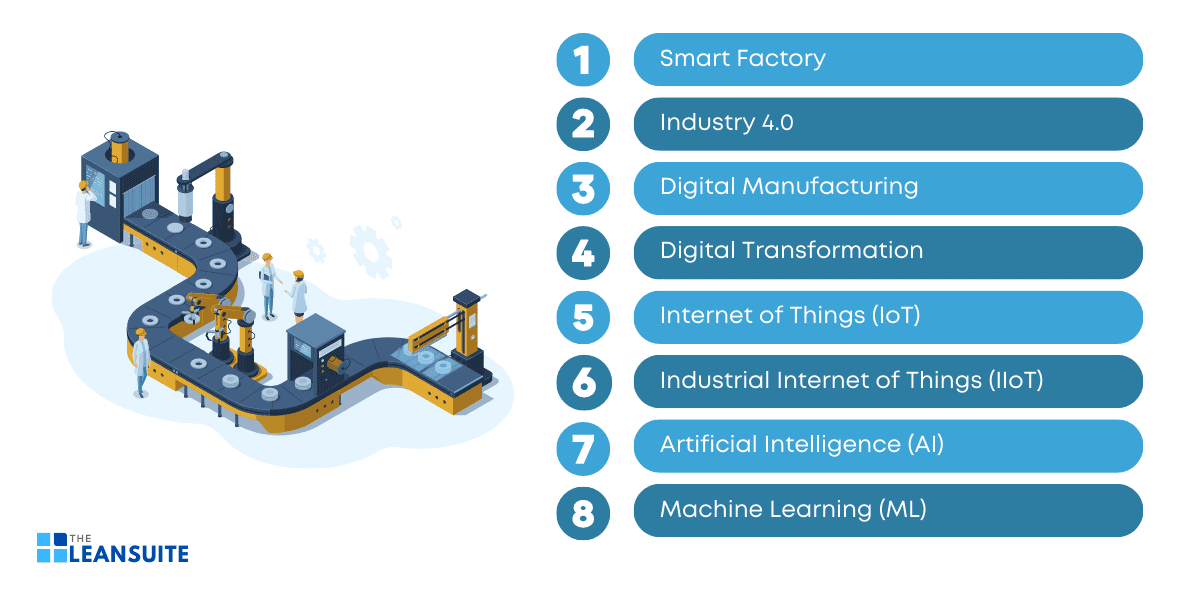
Nowadays, it seems as though whenever technology is mentioned online (or anywhere really), there is a new buzzword to learn about. Moreover, navigating them can be a nightmare. In this blog, we list eight basic industrial tech buzzwords you need to know and what they mean.
What are Some Basic Industrial Tech Buzzwords?
1. Smart Factory
The term smart factory has become one of the most increasingly used industrial tech buzzwords. It is a concept used to describe a highly digitized and connected environment where the application of different combinations of modern technologies is used to improve processes through automation and self-optimization. In other words, smart factories use up-to-date machinery and equipment to create new forms of efficiency and flexibility by connecting and streamlining different processes, information streams, and stakeholders (frontline workers, project managers, etc.). Because smart factories continuously improve the productivity of their manufacturing processes, they’re able to lower costs, reduce downtime, and minimize waste.
2. Industry 4.0
While industry 4.0 may just be another industrial tech buzzword, it actually represents the fourth revolution that has occurred in manufacturing. From the first industrial revolution (the ability to produce goods using water and steam power instead of just by hand) to the mass production using electricity and some degree of automation to manufacturing processes in the second, the fourth industrial revolution will take what was started in the third industrial revolution with the adoption of computers, advanced telecommunications and data analysis, and enhance it with an increase in automation and the employment of smart machines and smart factories. In short, industry 4.0 is driven by revolutionary trends such as the rise of data and connectivity, analytics, human-machine interaction, and improvements in robotics.
3. Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing refers to the integrated approach in manufacturing that uses technology to improve the efficiency of manufacturing operations. With digital manufacturing, manufacturers can create a factory that is a connected, networked and fully integrated environment. As a result, this enables them to use real-time data analytics to optimize their entire manufacturing process and significantly boost their productivity levels. Examples of use cases for digital manufacturing initiatives include:
- — Predictive maintenance to reduce and avoid costly breakdowns
- — Optimizing work stations to benefit the entire production line
- — Real-time asset tracking
4. Digital Transformation
The term digital transformation is one of the few industrial tech buzzwords listed in this blog that isn’t specific to just manufacturing — it can be used in — and applied to — any industry. A digital transformation is the process of leveraging digital technologies to modify existing, or create new, business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet the ever changing needs of businesses. Doing so can lead to improved efficiency, more business agility and, ultimately, an increase in new value for employees, customers, and shareholders.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical devices (or objects or things) that are embedded with sensors, software, network connectivity, and other technologies, allowing them to collect, connect, and share data with other devices and systems over the internet. For example, these devices can range from simple “smart home” devices like smart laundry machines to “smart wearable” devices such as smart watches and RFID-enabled clothing to complex industrial equipment and transportation systems. In essence, IoT enables these smart devices to communicate with each other and with other devices that use the internet like smartphones, creating a huge network of interconnected devices that can exchange data and complete a variety of tasks anonymously.
6. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Similar to the I0T, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is an industrial tech buzzword used to describe sensors, instruments, machines, and other devices that are networked together and use internet connectivity to enhance industrial and manufacturing business processes and operations. Essentially, the IIoT uses IoT technology in industrial applications. The data that is captured from these devices and technology are then analyzed to help increase visibility, enhance troubleshooting and maintenance capabilities, increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety and security.
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an industrial tech buzzword that has been floating around for some time. But now, it’s more popular than ever thanks to increased data volumes, advanced algorithms, and improvements in computing power and storage. Artificial intelligence refers to a machine’s ability to perform cognitive functions that only a human mind would normally be able to do. In essence, it makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs, and perform human-like tasks. For instance, some artificial intelligence examples include self-driving cars, facial recognition on smart phones, and marketing chatbots.
Artificial intelligence has become increasingly important in the manufacturing industry as it has the potential to transform it completely and provides many benefits. What’s more, it is said that artificial intelligence and manufacturing go hand in hand with each other since humans and machines work closely together in industrial manufacturing environments.
8. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning (ML) is an industrial tech buzzword that is closely related to artificial intelligence. In fact, machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence and computer science that uses data and algorithms to copy the way that humans learn, gradually improving its accuracy. In other words, it is the study of making machines more human in terms of behaviour and decision-making skills. That is to say, machine learning allows systems to learn, make decisions, and improve from experience without being specifically programmed. How it works is good quality data is inputted into the machines, and different algorithms are used to create machine learning models to train the machines on this data. The choice of algorithm depends on the type of data available and the type of activity that needs to be automated.
Like artificial intelligence, machine learning has the ability to transform the manufacturing industry as it can be used for quality control, automation, and customization. For example, before an end product reaches the customer, machine learning can be used to detect defects to ensure customer satisfaction. It can also be used to automate repetitive tasks such as assembly line work (like screwing a bolt onto a wheel) so that frontline workers can focus on other complex tasks.